Information
 Diabetes is a disease caused by the loss of the ability to transport
glucose into the cells of the body, either because not enough insulin
is produced or because the response to insulin is weak. Diabetes is a chronic, incapacitating disease affecting every organ system. There
are two major types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
Diabetes is a disease caused by the loss of the ability to transport
glucose into the cells of the body, either because not enough insulin
is produced or because the response to insulin is weak. Diabetes is a chronic, incapacitating disease affecting every organ system. There
are two major types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2.
In a healthy person, even a small rise in blood glucose stimulates the production and secretion of insulin, whose role is to increase glucose uptake into cells, returning the blood glucose to the optimal level. In diabetes, the blood stream may be awash with glucose, but it cannot reach the places where it is needed. The body can starve in the midst of plenty.

Type 1 Diabetes
Formally known as “insulin-dependent,” or “juvenile diabetes.” Type 1 diabetes is a life-long condition in which the pancreas stops making insulin. Insulin is a hormone that enables people to get energy from food. Without insulin, the body is not able to use glucose (blood sugar) for energy. To treat the disease, a person must inject insulin, follow a diet plan, exercise daily, and test blood sugar several times a day. Type 1 diabetes usually begins in the earlier stages of life.

Type 2 Diabetes
Formally known as “noninsulin-dependent” or “adult-onset diabetes.” Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes mellitus. About 90 to 95 percent of people who have diabetes have type 2 diabetes. People with type 2 diabetes produce insulin, but either do not make enough insulin or their bodies do not use the insulin they make. Most of the people who have this type of diabetes are overweight. Taking insulin does not cure any type of diabetes nor prevent the possibility of its eventual and devastating effects: kidney failure, blindness, nerve damage, amputation, heart attack, stroke, and pregnancy complications. Type 2 diabetes is mostly due to environmental factors.
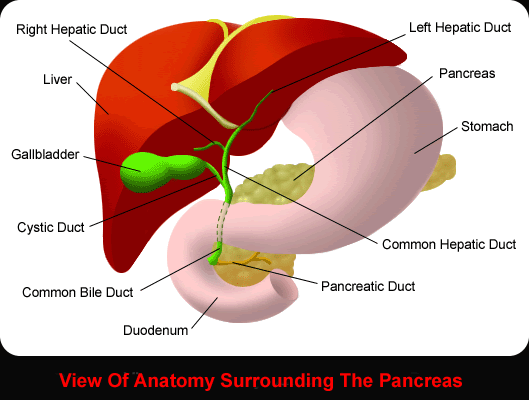
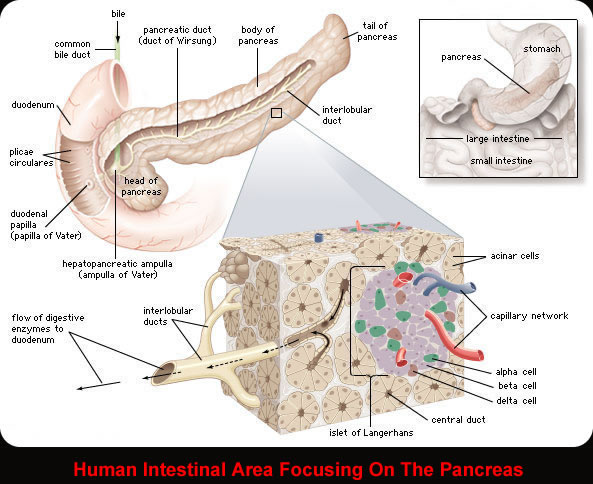
The Pancreas
- The pancreas is behind the stomach and the small intestine.
- It has three parts: head, body, and tail.
- The pancreas makes insulin and other hormones. It makes enzymes and fluids that help with digestion.
- The pancreas is connected to the small intestine by a tube called the pancreatic duct.
Insulin
Insulin is an hormone that informs the body's cells that the individual is properly fed, causing liver and muscle cells to take in glucose. The glucose is stored in the form of glycogen, which is used as energy. Glycogen causes fat cells to take in blood lipids and turn them into triglycerides, which play an important role in metabolism, using fat sources for energy.
Insulin is prescribed medically to treat some forms of diabetes mellitus. Individuals with type 1 diabetes mellitus depend on external insulin (most commonly injected below the skin) for their survival because of the absence of insulin. Those with type 2 diabetes mellitus have insulin resistance, relatively low insulin production, or both; some patients with type 2 diabetes may eventually require insulin when other medications become insufficient in controlling blood glucose levels.
